# Introduction to CSS ## The Presentation Layer --- ## What is CSS? CSS is a language for specifying how documents are presented to users — including fonts, colours and page layout. --- ## CSS syntax CSS is a rule-based language — you define the rules by specifying groups of styles that should be applied to particular elements or groups of elements on your web page. ``` p { color: red; padding: 24px; } ``` --- 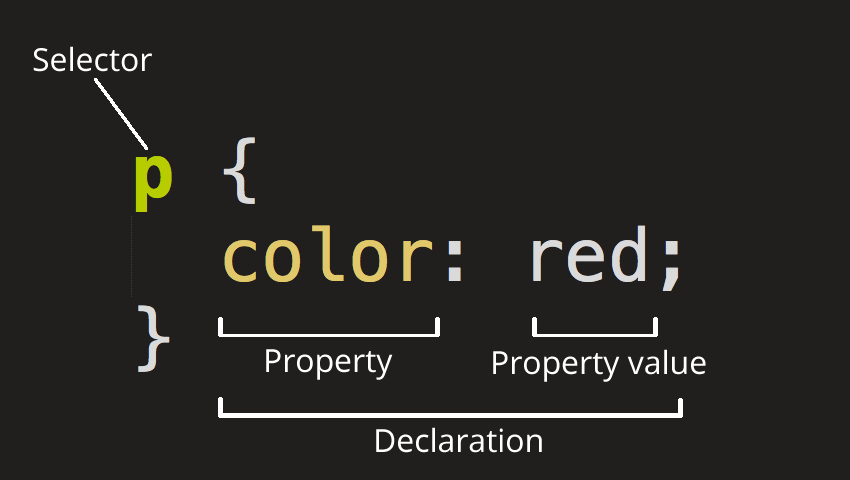 See: [CSS Basics](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Learn/Getting_started_with_the_web/CSS_basics) --- ## Selectors A CSS selector is the part of a CSS rule that describes what elements in a document the rule will match. The matching elements will have the rule's specified style applied to them. --- ## Type Selectors The CSS type selector matches elements by element name. ``` h1 { color: brown; border-bottom: 2px solid black; } ``` These declarations are applied to every `<h1>` element on the page. --- ## Class Selectors The CSS class selector matches elements based on the contents of their class attribute. HTML ```html <p class="intro">This is the story of my life...</p> <p>It was a dark and stormy night.</p> ``` CSS ```css .intro { font-style: italic; } ``` Only the first paragraph is italicized. --- ## Descendant Selector The descendant selectors combine two selectors such that elements matched by the second selector are selected if they have an ancestor (parent, parent's parent, parent's parent's parent, etc.) element matching the first selector. ```css /* List items that are descendants of the "my-things" list */ ul.my-things li { margin: 2em; } ``` --- ## Advanced Selectors There are many, many ways to select HTML elements with CSS. We've covered the ones that you'll use most of the time. See [Selector (CSS)](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Glossary/CSS_Selector) for a list of the rest. --- ## The Box Model 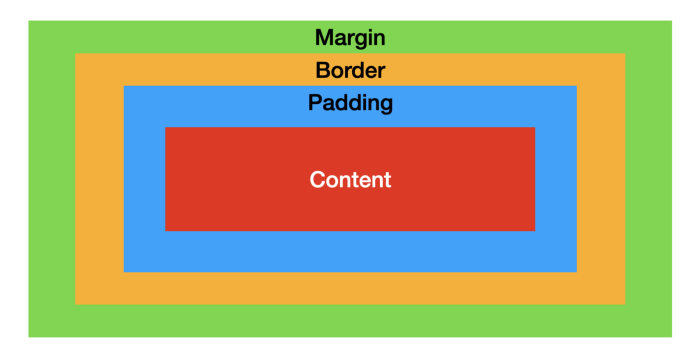 Source: [CSS: Box Model Explained](https://levelup.gitconnected.com/css-box-model-explained-60fc76fe9c4d) --- ## Box model properties These properties are commonly used to style the box model of HTML elements: - [`margin`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/margin) - [`border`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/border) - [`padding`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/padding) - [`background`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/border) - [`width`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/width) - [`max-width`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/max-width) --- ## Width: Key takeaways - Block-level elements (`<h1>`, `<p>`, `<div>`, etc) are 100% wide by default; - The `width` of inline elements (`<strong>`, `<em>`, `<a>`, etc) cannot be changed; - By default, `padding` and `border` are not included when the browser calculates an element's width. Use the following to include them: ```css body { box-sizing: border-box; } ``` --- ## Where does CSS go? There are three ways to add CSS to an HTML document: 1. [External stylesheet](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Learn/CSS/First_steps/How_CSS_is_structured#external_stylesheet) 2. [Internal stylesheet](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Learn/CSS/First_steps/How_CSS_is_structured#internal_stylesheet) 3. Inline style (not linked because it's bad practice for this course) --- ## Further Learning MDN CSS Introduction Guides: - [What is CSS?](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Learn/CSS/First_steps/What_is_CSS) - [Getting started with CSS](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Learn/CSS/First_steps/Getting_started) - [How CSS is structured](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Learn/CSS/First_steps/How_CSS_is_structured) - [How CSS works](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Learn/CSS/First_steps/How_CSS_works)